Tillage has been used since the beginning of agriculture to prepare the seedbed and reduce weeds that will compete with the crop. Tillage can be used in the spring, in-season, and after harvest as a single tactic weed management tool or in combination with other control tactics. The weeds present in any given field will reflect the tillage management system used; therefore, the weed community in a conventional tillage system will be very different than those in a no-till system.1
Tillage prior to planting
Control of weeds with tillage prior to planting is a major method to reduce weed density and is often referred to as primary tillage. Annual weed control can be greatly enhanced if primary tillage is used in combination with delayed planting, which allows the annual species to germinate prior to the tillage operation.2 However, if tillage is delayed to the point where weeds become larger, the effectiveness of tillage as a control tactic can be reduced. Summer annual weeds that are not killed by tillage can be more difficult to control with herbicides later in the season.3 Some examples of primary tillage implements are the moldboard plow and chisel plow, with the moldboard plow being more effective in burying weeds and weed seeds.
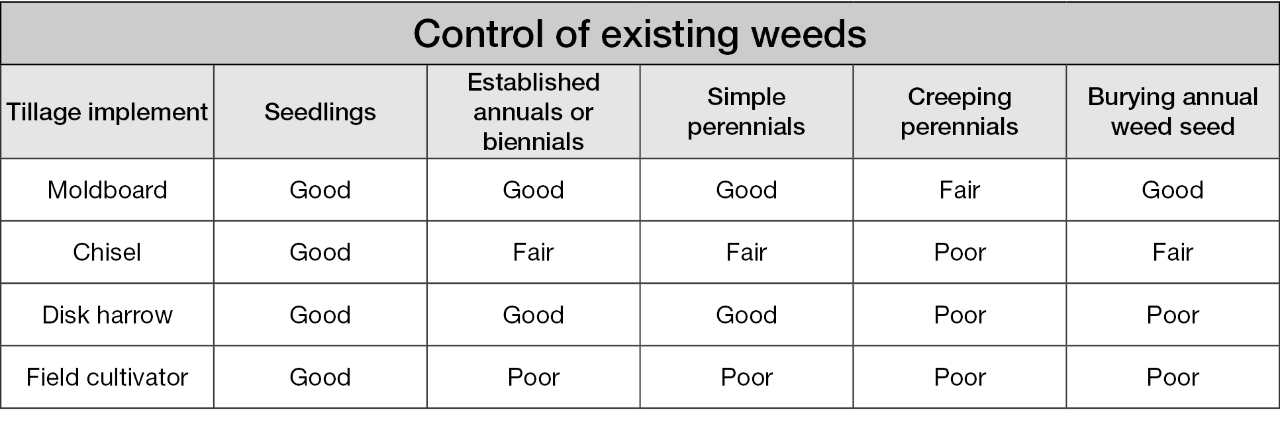
Secondary tillage is not as disruptive as primary tillage and is mainly used to prepare the seedbed. Secondary tillage will control small seedlings and germinating annual weeds by desiccation; therefore, it is best used when soil conditions are dry and temperatures are high. See Table 1 for which tillage operations are most effective in controlling weeds.
The stale seedbed system employs an early tillage operation to stimulate weed seed germination (usually 30 days prior to planting). This is followed by a secondary, usually light, tillage operation to destroy the emerging seedlings prior to planting. The use of the stale seedbed system can help deplete weed seed banks, but control of the weeds that germinate should be as complete as possible to prevent replenishing the bank.3
In addition to reducing growing weeds, primary and secondary tillage can change the distribution of weed seed in the soil profile, which can influence germination and seedling establishment. In some cases, seed can get buried to a depth that will not allow germination (moldboard plow) and in others it will bring seed to the surface providing an environment suitable for germination.3 See Table 2 for the optimum emergence depth of common weed species.

Generally, perennial and small-seeded weeds (i.e. lambsquarter) are more common in no-till systems as the roots of the perennials are undisturbed and small-seeded weed seeds are not buried below the germination depth. On the other hand, some large-seeded weeds (i.e. Pitted morningglory) left on the soil surface may not be able to successfully establish.3
Tillage after planting
There are two types of tillage used for weed control after planting: blind cultivation and inter-row cultivation. Blind cultivation is done without regard to the crop rows and is usually used to dislodge small weeds; the most common implement used is a rotary hoe. Plant size dictates the time limit on the use of blind cultivation. While corn and soybeans are good candidates for blind cultivation, small seed crops are not as they can become easily dislodged. Timing is critical for blind cultivation to be successful; the “white thread” stage (seed has germinated but not emerged) of weed seed germination is associated with the most consistent control.
Inter-row cultivation has become more precise and can be done with more speed with the advent of guidance support systems. While they were originally designed for low residue systems, over the past 20 years the equipment has been modified to be used in higher residue systems. Usually there is more time to utilize inter-row cultivation with row crops as compared to using blind cultivation.
Tillage can be used as a single tactic to manage weeds; however, using it in conjunction with other cultural and chemical tactics will provide a more consistent and sustainable weed management program.
Sources:
1Buhler, D. 1995. Influence of Tillage Systems on Weed Population Dynamics and Management in Corn and Soybean in the Central USA. Crop Science 35(5):1247-1258.
2Hager, A. 2013. Control Weeds Before Planting. University of Illinois Extension. The Bulletin. http://bulletin.ipm.illinois.edu/?p=385
3Cahoon, C., Curran, W. and Sandy, D. 2018. Pre- and Post-Plant Mechanical Weed Control. In Integrated Weed Management Guide for Mid-Atlantic Grain Crops. pp. 103 -127 https://integratedweedmanagement.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Integrated-Weed-Management-Manual.pdf
Sources verified 10/21/2019. 1016_S2
