Integrated weed management guidelines have been designed to address potential weed resistance and species shifts while sustaining high yield potential.
Herbicides with different sites of action and soil residual activity should be part of a weed management plan.
Alfalfa has several characteristics that can reduce the development of weed shifts and resistance.
Weed management should begin with a weed management plan that integrates several different weed control tactics. When considering herbicide applications, a variety of application timings (pre-plant, in-season, while dormant), and modes of action should be included. No single herbicide can control every weed present in an alfalfa field. While the advent of Roundup Ready® Alfalfa provided a new mode of action for control, it was not meant to replace existing modes of action and herbicide application timings, but to expand the options available to producers.
Alfalfa forage production methods have several characteristics that can help reduce both weed resistance and weed species shifts. As a competitive perennial crop with usually three to five years of production without soil disturbance, potential for weed seed germination is low. Cutting several times during the growing season reduces weed seed production, and the dormant period can allow additional weed management options for some production areas. At the same time, the lack of tillage, cultivation, and annual rotation can limit opportunities to control weeds. Managing weeds that occur in alfalfa and are resistant to glyphosate requires a balanced, integrated weed management plan (Table 1).
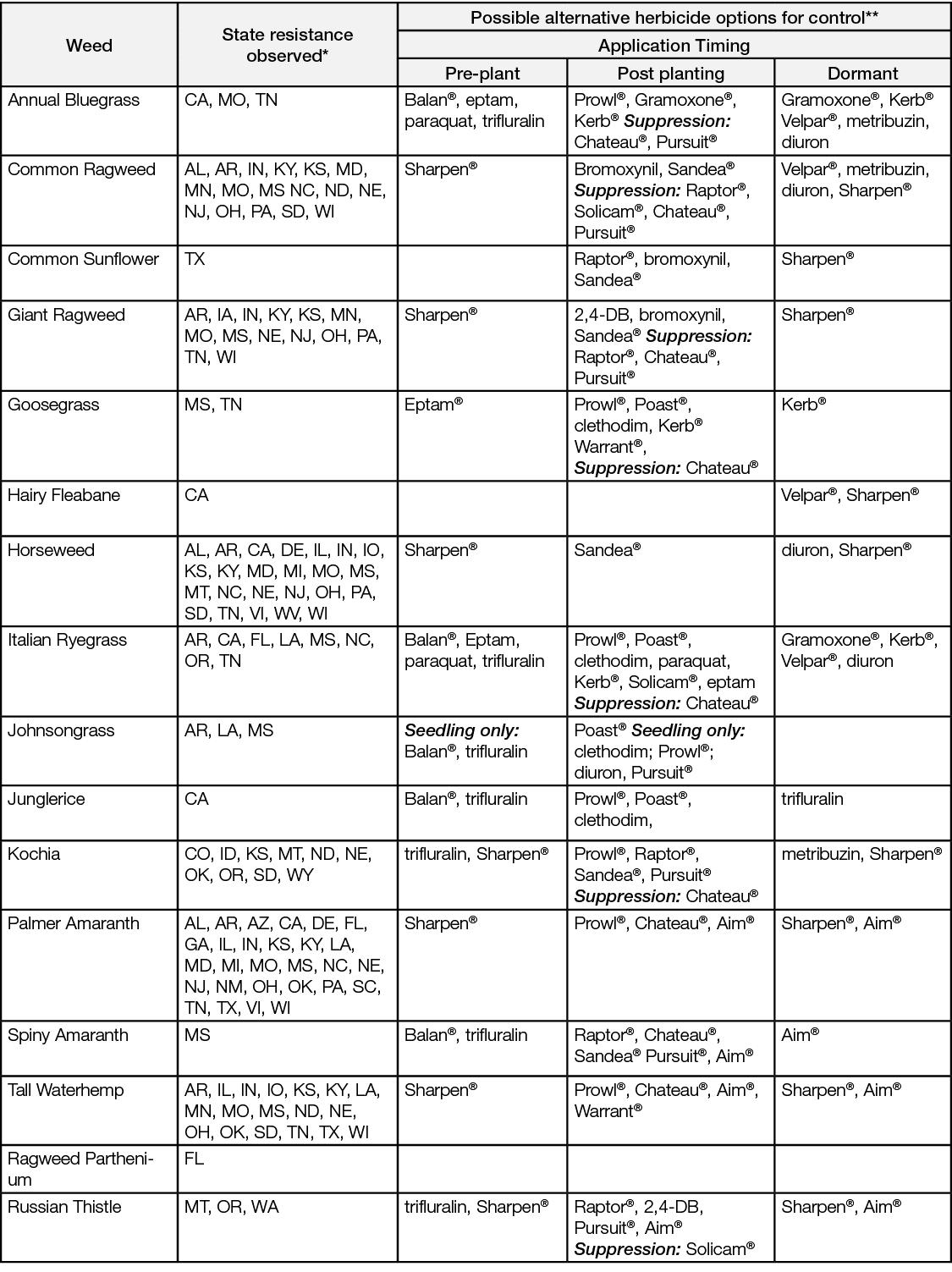 Table 1. Weeds found to be resistant to glyphosate, state resistant weeds are found, and possible alternative herbicide options for control.
Table 1. Weeds found to be resistant to glyphosate, state resistant weeds are found, and possible alternative herbicide options for control.
*Heap, I. The International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds. Online. Internet. Thursday, June 4, 2020 . Available www.weedscience.org
**Some herbicides may not be labeled for use in all states, consult with your local chemical provider and read and understand the label prior to use.
Establishing New Stands1,2
Weed infestations during crop establishment increases weed seed reserves and reduces seedling vigor and alfalfa stand. Forage quality can be reduced with decreased palatability and nutritional content. Some weed species can be toxic to livestock or cause irritation in the mouth, reducing intake. There are species of weeds, like those in the mustard family, that can impart an off flavor in milk as well.
Allowing weed establishment in new stands affects crop quality and yield potential throughout production of the crop. If protected from initial weed competition, a vigorous alfalfa stand can be very competitive against later-invading weeds. The use of a companion crop (nurse crop) such as field peas or oats can be used to suppress weed establishment. However, it is important not to plant too high of a planting rate that would allow the companion crop to compete for resources much like weeds would. The overall crop yield in the first year can be reduced with a companion crop. Shifting a planting date from early spring to late summer allows time for tillage to reduce weeds prior to seeding. However, planting too late may reduce the time required for alfalfa to establish well enough to outcompete winter annual weeds. For pre-plant application, Group 3 (benefin, trifluralin), Group 8 (EPTC), Group 14 (saflufenacil), and Group 22 (paraquat) herbicides can provide control over some of the key grass and broadleaf species with known resistance to glyphosate (Table 2).
 Table 2. Herbicide options for use in roundup ready alfalfa.
Table 2. Herbicide options for use in roundup ready alfalfa.
Newly Established Stand and In-Season Management1,2
There are many herbicide options available for application to newly-established stands that can control glyphosate-resistant weeds; however, timing with many products is critical. It is important to read and understand the specific use label prior to applying any herbicide. The products available include Group 1 (sethoxydim), Group 2 (halosulfuron, imazamox, imazethapyr, clethodim), Group 3 (pendimethalin, pronamide), Group 4 (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy), Group 6 (bromoxynil), Group 12 (norflurazon), Group 14 (carfentrazone, flumioxazin), Group 15 (acetochlor), and Group 22 (paraquat) herbicides (Table 2).
Grazing during late fall and into the winter dormant season can be effective in reducing weed growth and opening the stand to improve herbicide penetration to the soil surface after grazing. To limit soil compaction and injury to the crowns, it is recommended to use a large number of grazing animals over a short time period. Additionally, some weeds may increase risk of nitrate toxicity and others can be poisonous. Use of flaming can be used to reduce weed populations, but this method is typically most economical in smaller areas.
Dormant Stands
Managing Weed Species Shift
Continued reliance on a single weed management tactic can lead to a change in the frequency of a weed in the total weed population in a field. Herbicides do not equally control all weeds and if a product only controls a portion of the weed population, it can result in an increase of those that are not controlled. Utilizing multiple herbicides with different modes of action, integration of cultural weed control methods, and cutting the crop several times during the growing season can help reduce a weed shift in the population. Tank mixing herbicides with different modes of action will also help slow weed species shifts and manage possible resistant weed populations.
Use of Glyphosate with Roundup Ready® Alfalfa
Although there are currently over 15 weed species known to be resistant to glyphosate, not all of them are commonly found in alfalfa, or distributed across the alfalfa production area. Roundup Ready® Alfalfa provides increased herbicide timing flexibility when compared to other products available. To maximize the benefit of Roundup Ready Alfalfa, apply glyphosate to seedling alfalfa at the three to five trifoliate stage and when weeds are less than 4-inches tall. Applications can also be made in-season after cutting and up to five days prior to the next cutting.
Summary of Ideas for Managing Weeds in Roundup Ready® Alfalfa
Develop a weed management program based on your agronomic situation and forage production needs.
Monitor weed populations for species shifts and inadequate control after correct application.
Control problem weeds prior to planting and prepare a proper seedbed to ensure even germination and emergence.
Utilize different herbicide application timings and modes of action in the herbicide program.
Maintain proper soil nutrition to facilitate competitive growth.
Alter cutting schedules and consider longer cycles to allow alfalfa to remain vigorous.
Control insects and diseases to help maintain a healthy competitive stand.
Sources
1 Cavenari, M., Vargas, R.N, and Orloff, S. 2007. Weed management in alfalfa. University of California Extension. https://wric.ucdavis.edu/PDFs/WeedManagementInAlfalfa.pdf.
2 Lingenfelter, D. 2020. Spring weed control in alfalfa. Pennsylvania State University Extension. https://extension.psu.edu/spring-weed-control-in-alfalfa.
4020_S1
